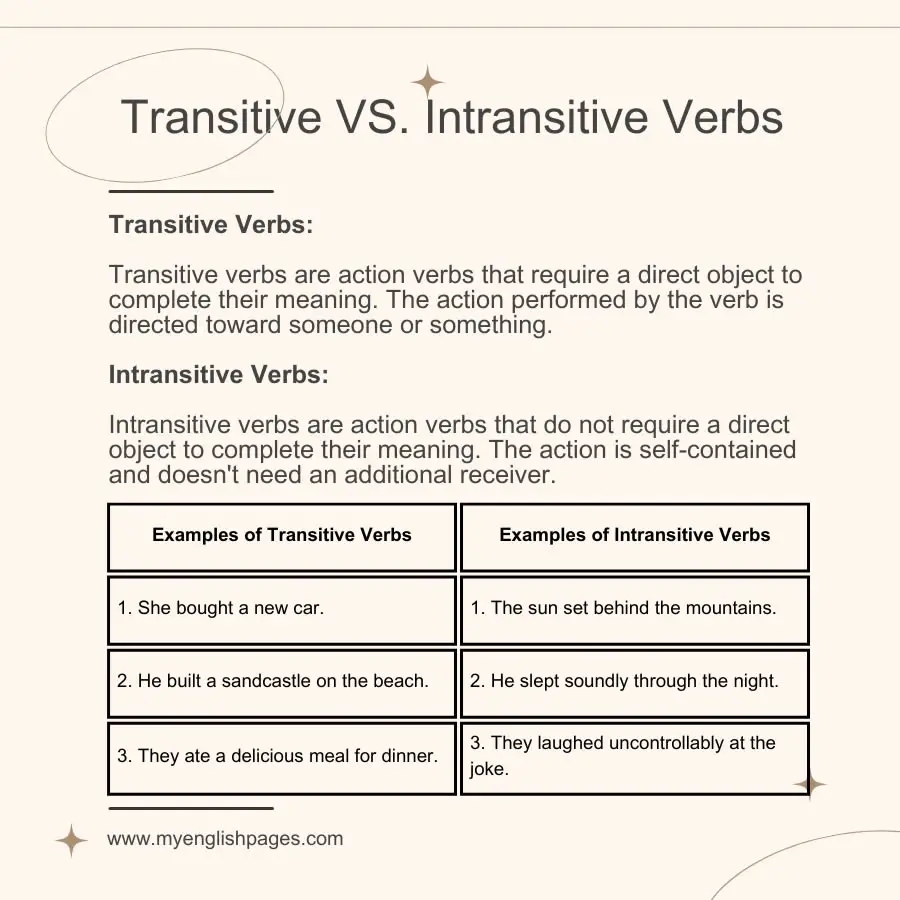
Transitive verbs are verbs that require a direct object to complete their meaning. They are action verbs that transfer their action to a receiver. In other words, transitive verbs have both a subject performing the action and a direct object receiving the action. Here, we will explore 10 examples of transitive verbs.
Transitive verbs can be identified by asking the question “what” or “whom” after the verb. If the answer is a noun or pronoun, then the verb is transitive. These verbs are essential in constructing meaningful sentences and conveying clear actions.
It is important to note that transitive verbs can also be used in passive voice constructions where the subject receives the action rather than performs it. For example, “The cake was eaten by her” or “A new house was built in the neighborhood.” In these sentences, the direct object becomes the subject of the sentence.
By understanding and using transitive verbs effectively, writers and speakers can communicate their actions and intentions clearly. Whether describing a simple daily activity or a complex project, transitive verbs play a crucial role in conveying meaning in language.
In conclusion, transitive verbs are an essential part of grammar and language usage. By incorporating them into our writing and speech, we can create more precise and impactful communication. Practice using transitive verbs in your sentences to enhance clarity and expressiveness in your language.