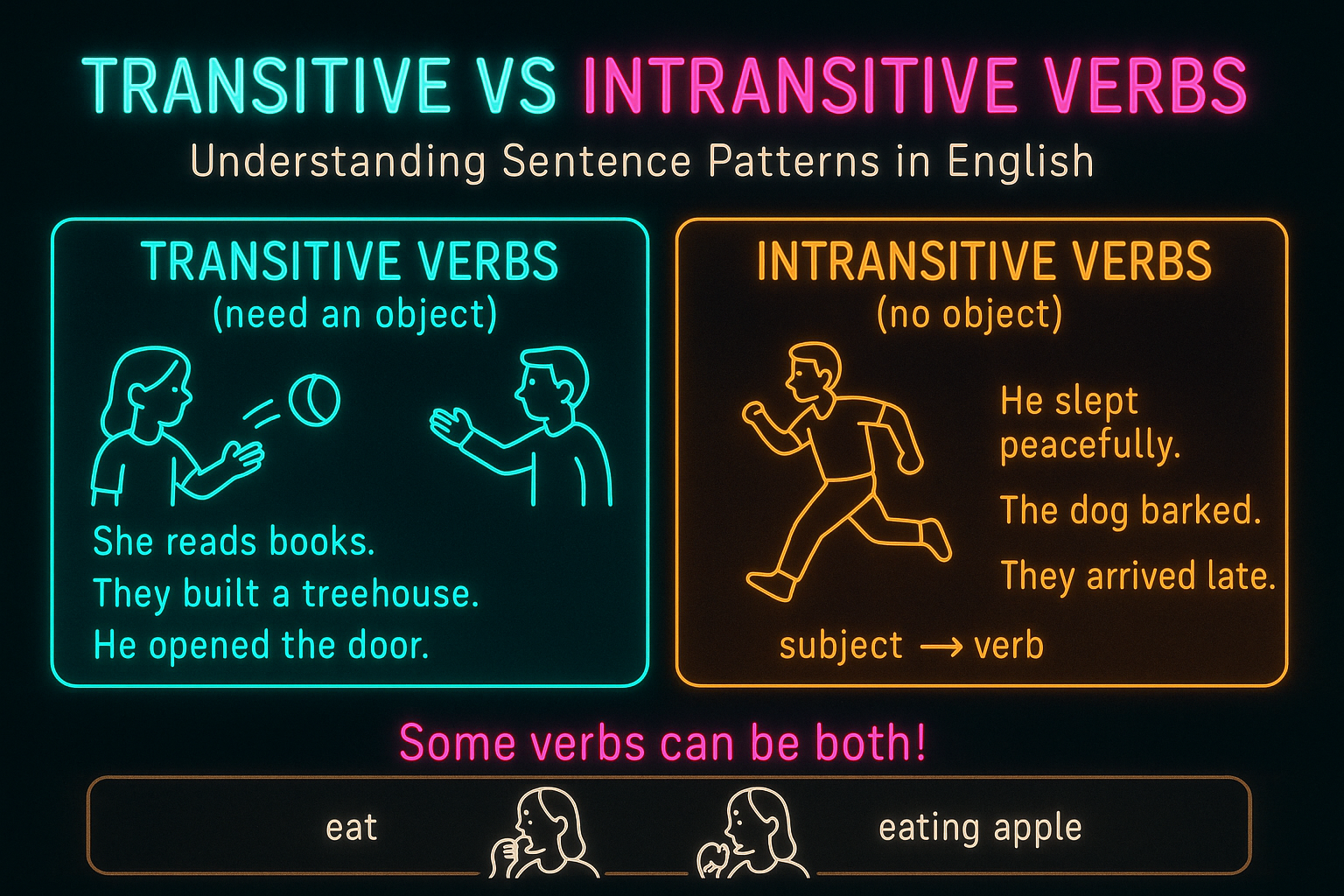
Verbs are an essential part of any sentence, as they convey the action being performed. However, not all verbs function in the same way. Intransitive and transitive verbs are two distinct categories that dictate how the action is carried out in a sentence. Understanding the difference between these two types of verbs is crucial for constructing clear and concise sentences.
Intransitive and transitive verbs are distinguished by the number of objects they require in a sentence. Intransitive verbs do not require an object to complete their meaning, while transitive verbs do. This fundamental difference affects the structure and meaning of a sentence, making it important to use the correct type of verb in the appropriate context.
Difference Between Intransitive and Transitive
One key difference between intransitive and transitive verbs is the presence of an object. Intransitive verbs do not take a direct object, as they express a complete action without requiring any additional information. For example, in the sentence “She sleeps,” the verb “sleeps” is intransitive because it conveys a complete action without needing an object.
On the other hand, transitive verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning. These verbs transfer the action to a recipient, indicating who or what is affected by the action. For instance, in the sentence “He read a book,” the verb “read” is transitive because it needs the object “a book” to convey the action being performed.
Another distinction between intransitive and transitive verbs lies in their ability to be transformed into passive voice. Intransitive verbs cannot be converted into passive voice, as they do not have a direct object to become the subject of the passive construction. Transitive verbs, however, can be transformed into passive voice by making the object the subject of the sentence. This difference demonstrates how the presence of an object impacts the grammatical structure of a sentence.
In summary, the difference between intransitive and transitive verbs lies in the requirement of a direct object. Intransitive verbs do not need an object to convey a complete action, while transitive verbs require an object to complete their meaning. Understanding this distinction is essential for constructing grammatically correct sentences and conveying clear communication.
By recognizing the difference between intransitive and transitive verbs, writers can enhance the clarity and effectiveness of their writing. Choosing the appropriate verb type based on the presence of an object is crucial for conveying the intended meaning and structure of a sentence. Mastering the usage of intransitive and transitive verbs will enable writers to communicate more effectively and create well-structured sentences.