In English grammar, verbs can be classified as either intransitive or transitive. Understanding the distinction between these two types of verbs is essential for constructing clear and concise sentences. Intransitive and transitive verbs have different roles in a sentence, and knowing how to use them correctly can greatly improve your writing skills.
Let’s explore the characteristics of intransitive and transitive verbs and how they function within a sentence.
Intransitive and Transitive Verbs
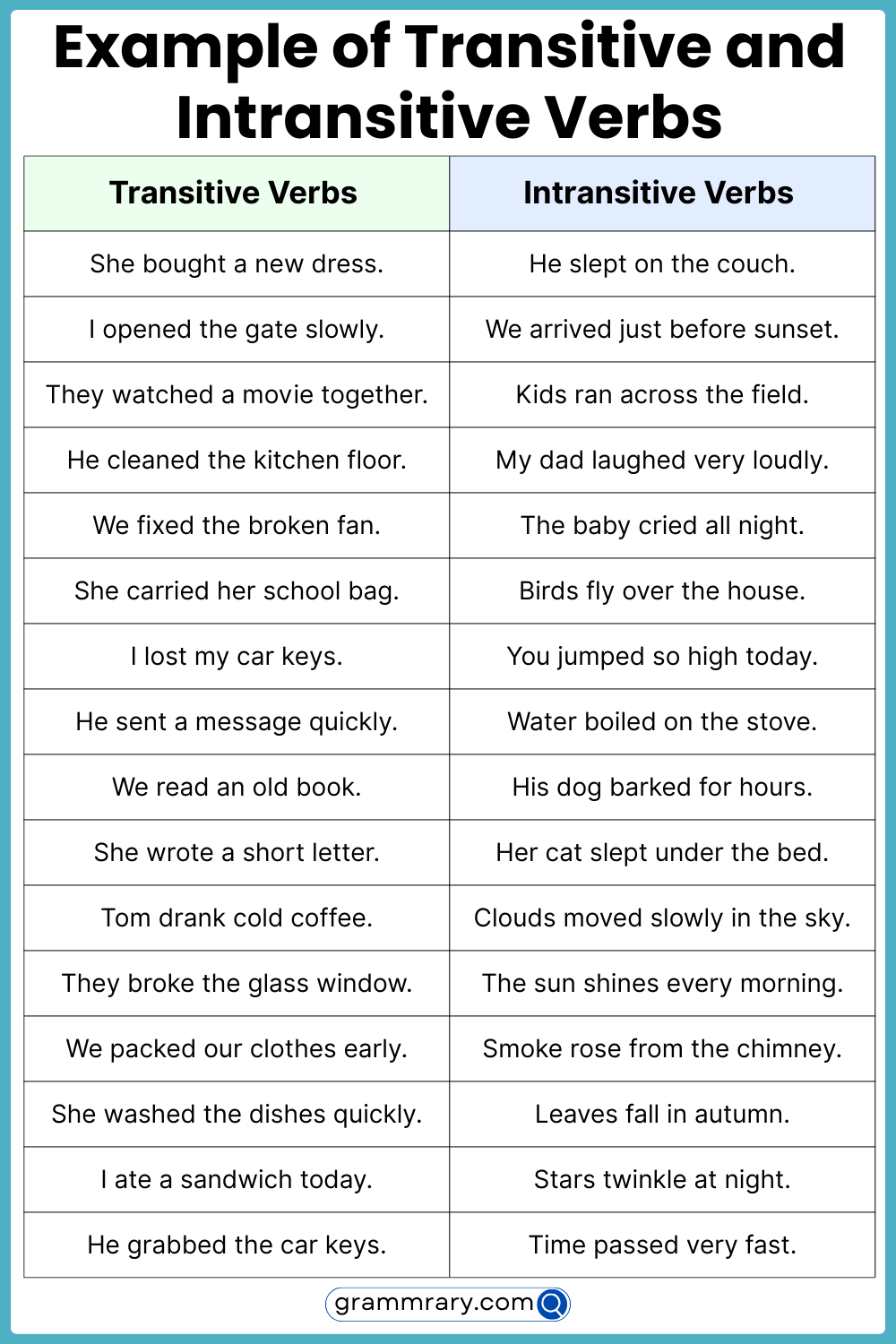
Intransitive Verbs: Intransitive verbs are action verbs that do not require a direct object to complete their meaning. These verbs express an action that is complete in itself and does not transfer the action to an object. For example, in the sentence “She sleeps peacefully,” the verb “sleeps” is intransitive because it does not require a direct object.
Transitive Verbs: Transitive verbs are action verbs that require a direct object to complete their meaning. These verbs transfer the action to an object, which receives the action of the verb. For example, in the sentence “She reads a book,” the verb “reads” is transitive because it requires the direct object “book” to complete the action.
Transitive verbs can be followed by one or more objects, while intransitive verbs do not have a direct object following them. Understanding the distinction between these two types of verbs is crucial for constructing grammatically correct sentences.
It is important to note that some verbs can be both transitive and intransitive, depending on how they are used in a sentence. For example, the verb “eat” can be transitive when followed by a direct object (e.g., “She eats an apple”) or intransitive when used without a direct object (e.g., “She eats quickly”).
Overall, mastering the use of intransitive and transitive verbs can enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your writing. By understanding the roles that these verbs play in a sentence, you can create more precise and meaningful sentences that effectively communicate your ideas.
In conclusion, intransitive and transitive verbs serve distinct functions in English grammar. Intransitive verbs do not require a direct object, while transitive verbs do. By recognizing the differences between these two types of verbs, you can improve your writing skills and create more cohesive and structured sentences.