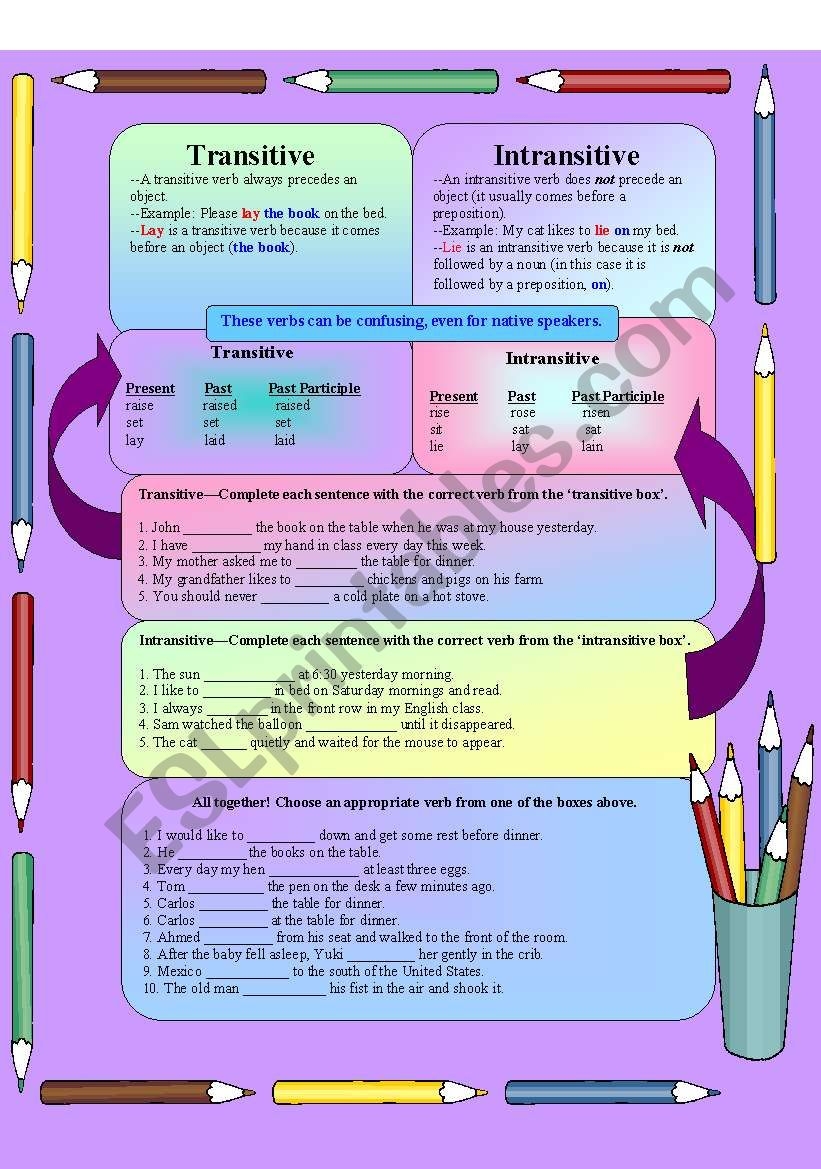
Verbs are an essential part of any sentence, as they express the action or state of being. In class 7, students are introduced to the concept of transitive and intransitive verbs, which play a vital role in sentence construction.
Transitive and intransitive verbs are two different types of verbs that require different sentence structures. Understanding the difference between these two types of verbs is crucial for students to improve their grammar and writing skills.
Transitive and Intransitive Verb Class 7
Transitive verbs are action verbs that require a direct object to complete their meaning in a sentence. For example, in the sentence “She ate an apple,” the verb “ate” is transitive because it requires the direct object “an apple” to make sense.
In contrast, intransitive verbs do not require a direct object to complete their meaning. These verbs express action or describe a state of being without needing an object. For example, in the sentence “He sleeps peacefully,” the verb “sleeps” is intransitive because it does not require a direct object.
It is important for students to identify whether a verb is transitive or intransitive to construct grammatically correct sentences. By understanding the difference between these two types of verbs, students can avoid common grammatical errors and improve their writing skills.
Transitive verbs can often be identified by asking the question “what” or “whom” after the verb. If the answer to the question is a noun or pronoun, then the verb is transitive. Intransitive verbs, on the other hand, do not require a direct object and do not answer these questions.
Practicing with examples and exercises can help students grasp the concept of transitive and intransitive verbs more effectively. By recognizing the patterns and structures of these verbs in sentences, students can enhance their language skills and communicate more clearly.
In conclusion, understanding transitive and intransitive verbs is essential for class 7 students to improve their grammar and writing abilities. By recognizing the differences between these two types of verbs and practicing with examples, students can enhance their language proficiency and develop stronger communication skills.