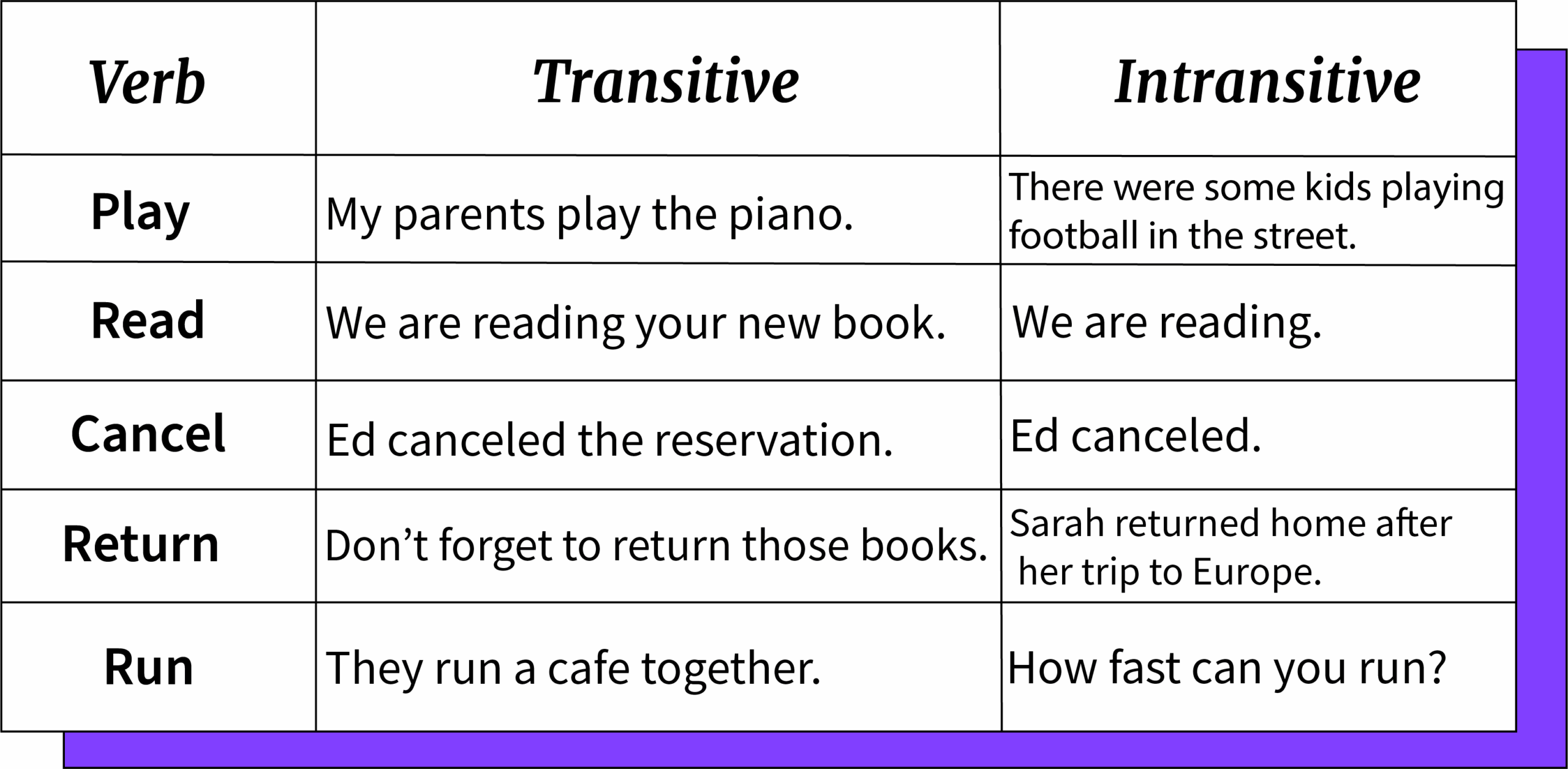
Transitive verbs are a crucial part of the English language and play a significant role in forming meaningful sentences. These verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning, unlike intransitive verbs that do not require an object. By understanding transitive verbs and their examples, you can enhance your writing and communication skills.
Transitive verbs are action verbs that are followed by a direct object, which receives the action of the verb. They answer the question “what?” or “whom?” after the verb. For example, in the sentence “She read a book,” the transitive verb is “read,” and the direct object is “a book.” Without the direct object, the sentence would be incomplete.
Transitive Verbs Examples
1. Eat: She ate a delicious meal.
2. Throw: He threw the ball to his friend.
3. Write: I wrote a letter to my grandmother.
4. Paint: She painted a beautiful picture on the canvas.
5. Build: The construction workers built a new bridge over the river.
Transitive verbs can be simple or complex, but their main characteristic is the need for a direct object to complete the sentence’s meaning. Using transitive verbs effectively can make your writing more concise and engaging.
It is essential to identify transitive verbs in sentences to ensure clarity and coherence. By recognizing transitive verbs and their direct objects, you can construct meaningful and grammatically correct sentences. Practice using transitive verbs in your writing to improve your language skills and convey your message effectively.
In conclusion, transitive verbs are an integral part of English grammar and sentence structure. By incorporating transitive verbs into your writing, you can create more dynamic and descriptive sentences. Understanding transitive verbs and their examples will help you communicate more effectively and express your ideas with precision.