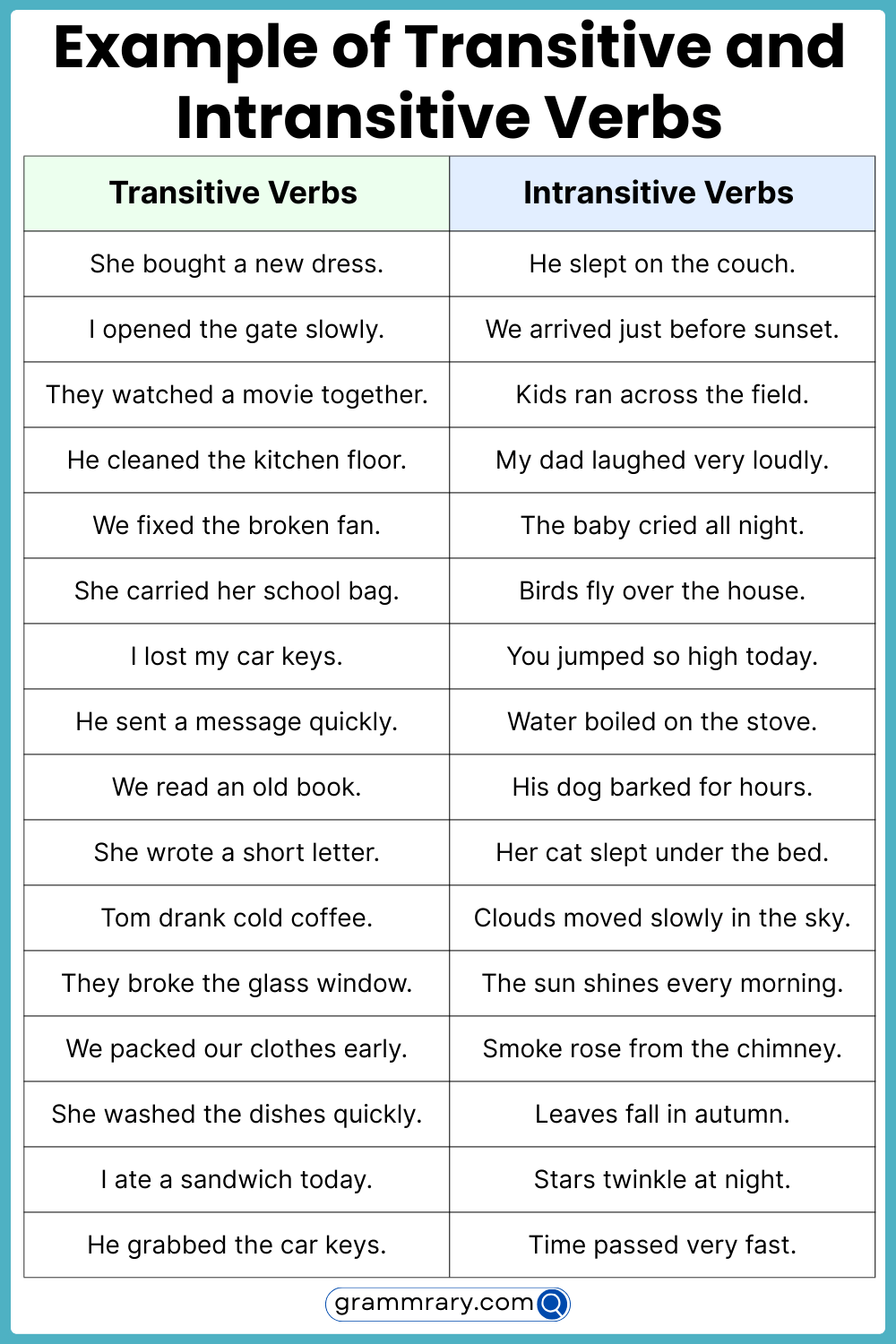
Verbs are an essential part of any sentence, as they express actions or states of being. Understanding the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs is crucial for constructing grammatically correct sentences.
Transitive verbs require an object to complete their meaning, while intransitive verbs do not. This distinction plays a significant role in sentence structure and comprehension.
Transitive versus Intransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are action verbs that require a direct object to complete their meaning. For example, in the sentence “She ate the apple,” the verb “ate” is transitive because it requires the direct object “the apple” to make sense.
Intransitive verbs, on the other hand, do not require a direct object to complete their meaning. For example, in the sentence “He slept peacefully,” the verb “slept” is intransitive because it does not need a direct object to convey its meaning.
Transitive verbs can also be followed by indirect objects, which receive the action of the verb indirectly. For example, in the sentence “I gave her a book,” the verb “gave” is transitive, with “her” being the indirect object receiving the book.
Intransitive verbs, however, do not take direct or indirect objects. They typically express actions or states that do not transfer to an object. For example, in the sentence “The sun rises in the east,” the verb “rises” is intransitive because it does not act upon a direct object.
It is important to note that some verbs can function as both transitive and intransitive, depending on how they are used in a sentence. For example, the verb “run” can be transitive in the sentence “She ran the marathon” or intransitive in the sentence “He runs every morning.”
Understanding the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs is essential for constructing clear and concise sentences. By recognizing whether a verb requires a direct object or not, writers can avoid grammatical errors and improve the overall quality of their writing.
In conclusion, transitive verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning, while intransitive verbs do not. By mastering the use of both types of verbs, writers can effectively convey their intended message and create well-structured sentences.