Verbs are an essential part of any sentence as they indicate actions or states of being. They are often referred to as the “action words” in a sentence. Understanding verbs and their tenses is crucial for effective communication and clarity in writing.
Verbs come in various forms and can change based on the tense, mood, voice, and aspect of the sentence. Tenses help to indicate the time at which an action took place, whether it is in the past, present, or future.
Verb and Verb Tenses
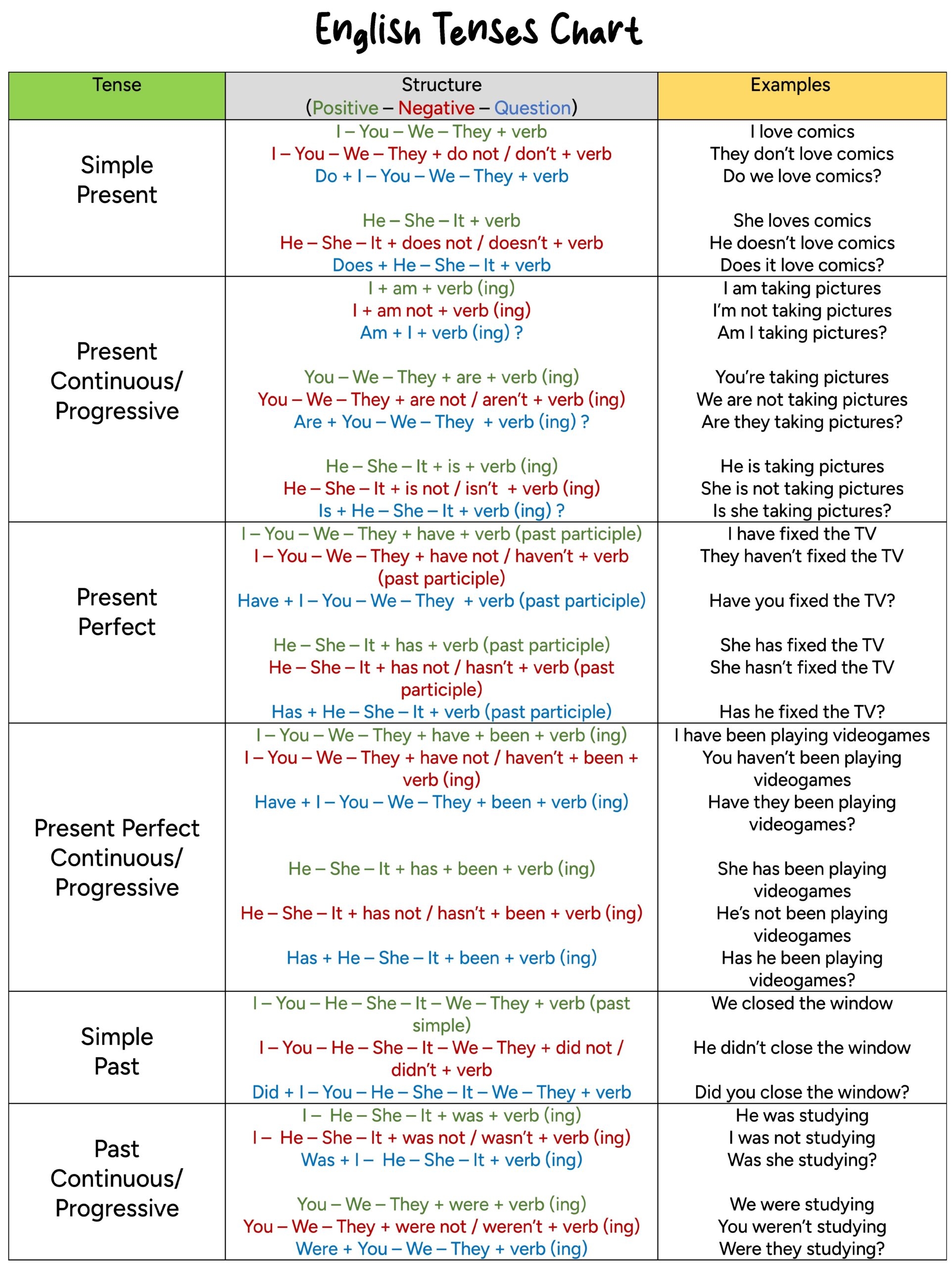
There are three main verb tenses: past, present, and future. Each tense has its own set of rules and forms that dictate how the verb should be used in a sentence. Understanding these tenses is key to constructing grammatically correct sentences.
The past tense is used to describe actions that have already happened. For example, “She walked to the store yesterday.” The present tense is used to describe actions that are currently happening or are habitual. For example, “She walks to the store every day.” The future tense is used to describe actions that will happen in the future. For example, “She will walk to the store tomorrow.”
It is important to note that verbs can also be conjugated to indicate different aspects such as progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive. These aspects add more detail to the action being described. For example, “She is walking to the store” (progressive), “She has walked to the store” (perfect), and “She has been walking to the store” (perfect progressive).
When writing, it is crucial to use the correct verb tense to ensure clarity and accuracy in communication. Mixing tenses can lead to confusion and misunderstanding. Practice and familiarity with verb tenses can help improve writing skills and overall communication.
In conclusion, verbs and their tenses play a vital role in constructing meaningful sentences. By understanding the different verb forms and tenses, one can effectively communicate ideas and actions in writing. Practice and attention to detail are key in mastering the use of verbs in various contexts.