In grammar, verbs are classified into different categories based on their usage and structure. One such category is transitive verbs. Transitive verbs are action verbs that require a direct object to complete their meaning.
Transitive verbs are an essential part of sentence construction as they indicate the action being performed and the recipient of that action. Understanding transitive verbs can help improve the clarity and effectiveness of your writing.
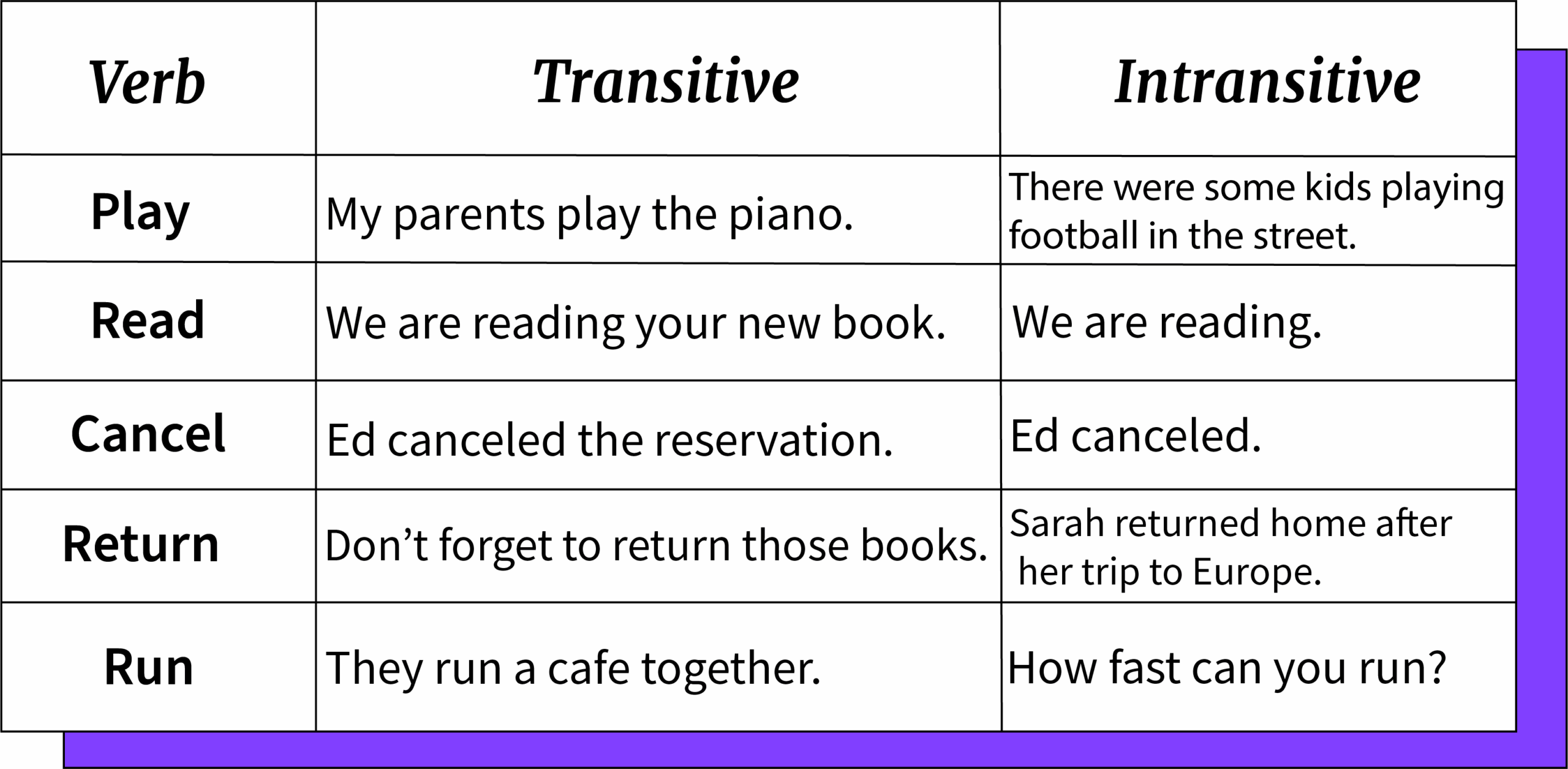
Verb Transitive
Transitive verbs are verbs that require a direct object to complete their meaning. This means that the action performed by the verb is done to someone or something. For example, in the sentence “She ate the apple,” the verb “ate” is transitive because it requires a direct object (the apple) to make sense.
Transitive verbs can be easily identified by asking the question “What?” or “Whom?” after the verb. If there is an answer to these questions, then the verb is transitive. For example, in the sentence “He read a book,” you can ask “He read what?” The answer is “a book,” making “read” a transitive verb.
Transitive verbs play a crucial role in sentence structure by connecting the subject to the object and conveying the action that is being performed. Using transitive verbs effectively can make your writing more concise and impactful.
It is important to note that not all verbs are transitive. Intransitive verbs, on the other hand, do not require a direct object to complete their meaning. For example, in the sentence “She slept peacefully,” the verb “slept” is intransitive as it does not require a direct object.
When using transitive verbs, it is essential to ensure that the direct object is placed correctly in the sentence to avoid confusion or ambiguity. Always remember that transitive verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning and convey the action effectively.
In conclusion, understanding and using transitive verbs correctly can enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your writing. By identifying transitive verbs and their direct objects, you can create more concise and impactful sentences that clearly convey the action being performed.