Nouns are an essential part of speech that help us identify people, places, things, and ideas in our language. They serve as the building blocks of sentences, providing the subjects and objects that make up the core of communication. A noun can be a single word or a group of words that function as a unit in a sentence.
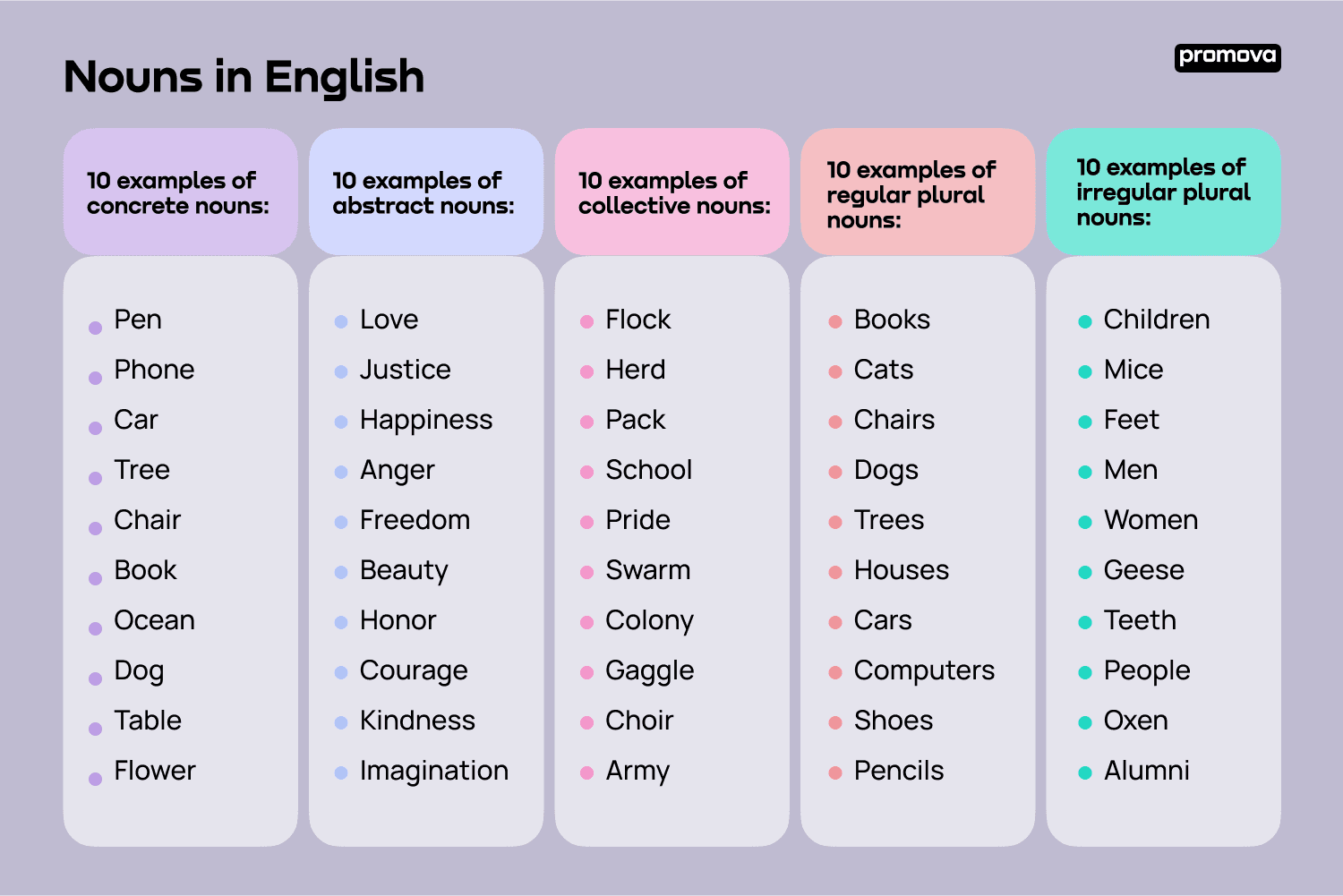
When we use a noun, we are essentially giving a name to something in the world around us. This name helps us to distinguish one thing from another and to communicate effectively with others. Nouns can be concrete, such as “car” or “tree,” or abstract, such as “love” or “happiness.” They can also be common, like “dog” or “house,” or proper, like “Rover” or “Paris.”
Types of Nouns
Nouns can be categorized into several different types, depending on their function and form. Common types of nouns include:
1. Proper Nouns: These nouns refer to specific, unique entities and are always capitalized. Examples include “John,” “London,” and “Toyota.”
2. Common Nouns: These nouns refer to general, non-specific entities and are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence. Examples include “dog,” “city,” and “car.”
3. Countable Nouns: These nouns can be counted and have both singular and plural forms. Examples include “apple” (singular) and “apples” (plural).
4. Uncountable Nouns: These nouns cannot be counted and do not have a plural form. Examples include “water,” “furniture,” and “information.”
5. Collective Nouns: These nouns refer to groups of people or things. Examples include “team,” “family,” and “herd.”
In conclusion, nouns play a crucial role in our language by providing names for the people, places, things, and ideas that we encounter in our daily lives. By understanding the different types of nouns and how they function in sentences, we can improve our communication skills and express ourselves more clearly. So the next time you come across a noun, remember that it’s giving a name to something in the world around you.