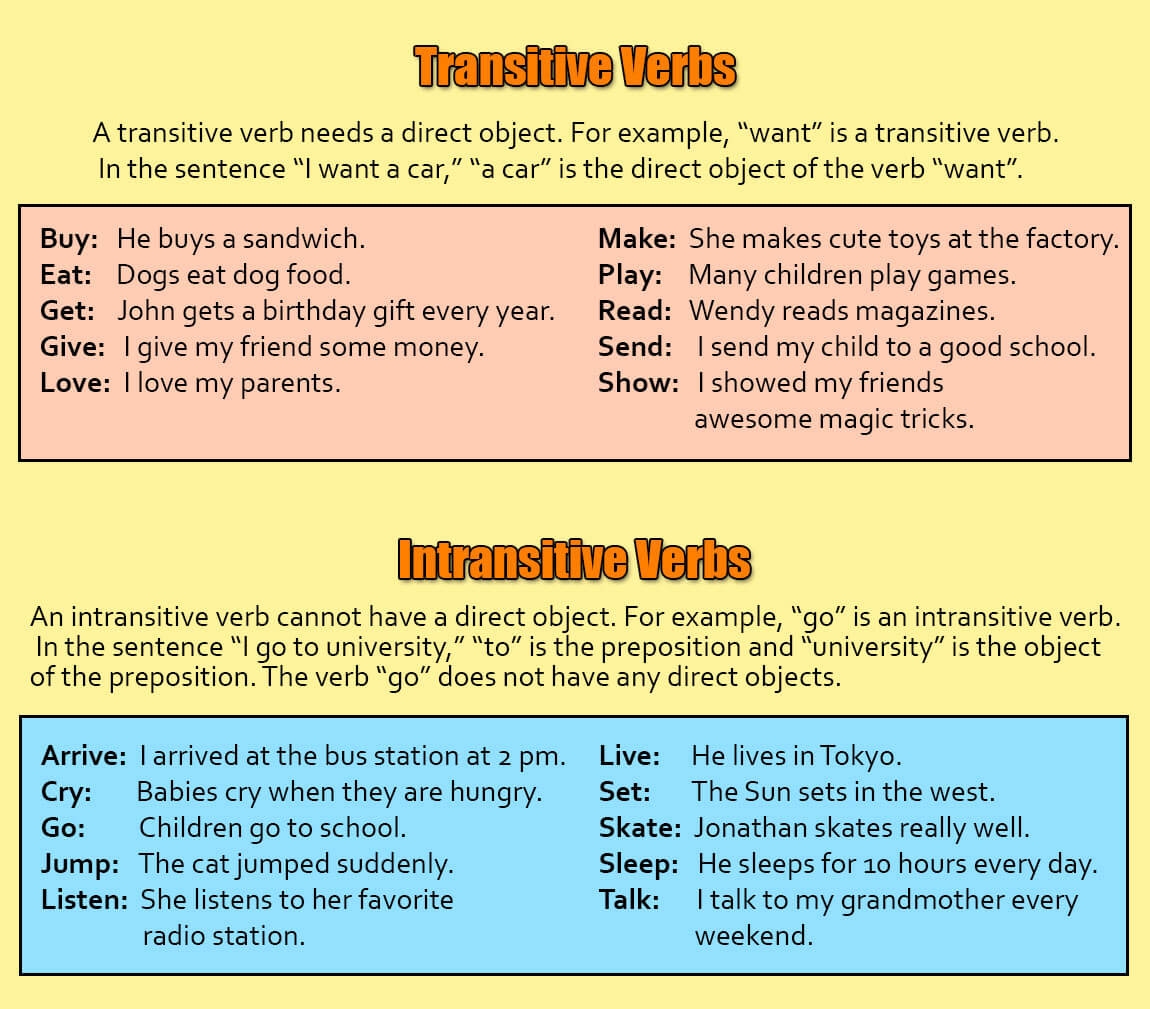
Verbs are an essential part of language, helping to convey action or state of being in a sentence. In grammar, verbs can be classified as either transitive or intransitive, depending on whether they require an object to complete their meaning. Understanding what makes a verb transitive is crucial for mastering language skills.
Transitive verbs are those that require a direct object to complete their meaning in a sentence. This means that the action of the verb is directed towards an object. For example, in the sentence “She ate an apple,” the verb “ate” is transitive because it requires the object “apple” to make sense.
Characteristics of Transitive Verbs
One characteristic that makes a verb transitive is that it can be followed by a direct object. This direct object is the recipient of the action performed by the verb. For instance, in the sentence “He kicked the ball,” the verb “kicked” is transitive because it is followed by the direct object “ball.”
Another characteristic of transitive verbs is that they can be transformed into the passive voice. In passive constructions, the object of the verb becomes the subject of the sentence. For example, in the passive sentence “The ball was kicked by him,” the transitive verb “kicked” is still followed by the direct object “ball.”
Transitive verbs can also be used in causative constructions, where the subject of the verb causes someone or something else to perform the action. For example, in the sentence “She made him laugh,” the transitive verb “made” is followed by the direct object “him,” who is the one performing the action of laughing.
It is important to note that not all verbs can be transitive. Intransitive verbs, for example, do not require a direct object to complete their meaning. Understanding the characteristics of transitive verbs can help learners identify and use them correctly in sentences.
In conclusion, what makes a verb transitive is its ability to require a direct object to complete its meaning in a sentence. Transitive verbs exhibit certain characteristics, such as being followed by a direct object, being able to be transformed into the passive voice, and being used in causative constructions. By recognizing these features, language learners can improve their understanding and usage of transitive verbs in communication.